
 |

|
| ActiveWin: Reviews | Active Network | New Reviews | Old Reviews | Interviews |Mailing List | Forums |
|
|
|
|
|
DirectX |
|
ActiveMac |
|
Downloads |
|
Forums |
|
Interviews |
|
News |
|
MS Games & Hardware |
|
Reviews |
|
Support Center |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2003 |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows XP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News Centers |
|
Windows/Microsoft |
|
DVD |
|
Apple/Mac |
|
Xbox |
|
News Search |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveXBox |
|
Xbox News |
|
Box Shots |
|
Inside The Xbox |
|
Released Titles |
|
Announced Titles |
|
Screenshots/Videos |
|
History Of The Xbox |
|
Links |
|
Forum |
|
FAQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Windows XP |
|
Introduction |
|
System Requirements |
|
Home Features |
|
Pro Features |
|
Upgrade Checklists |
|
History |
|
FAQ |
|
Links |
|
TopTechTips |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAQ's |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows 98/98 SE |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2002 |
|
Windows "Whistler" XP |
|
Windows CE |
|
Internet Explorer 6 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Xbox |
|
Xbox 360 |
|
DirectX |
|
DVD's |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TopTechTips |
|
Registry Tips |
|
Windows 95/98 |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Program Tips |
|
Easter Eggs |
|
Hardware |
|
DVD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveDVD |
|
DVD News |
|
DVD Forum |
|
Glossary |
|
Tips |
|
Articles |
|
Reviews |
|
News Archive |
|
Links |
|
Drivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Reviews |
|
Xbox/Games |
|
Fallout 3 |
|
|
|
Applications |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|
Windows 7 |
|
|
|
Hardware |
|
iPod Touch 32GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Interviews |
|
Steve Ballmer |
|
Jim Allchin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Site News/Info |
|
About This Site |
|
Affiliates |
|
Contact Us |
|
Default Home Page |
|
Link To Us |
|
Links |
|
News Archive |
|
Site Search |
|
Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credits |


|
Product: Windows XP Professional Company: Microsoft Website: http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp Estimated Street Price: Upgrade $199.99 - Full $299.99 Review By: Julien Jay |
Networking
|
Table Of Contents |
Microsoft Windows XP Professional comes with tons of networking features just like Windows 2000. First the NETBEUI protocol has been ditched so if you really want to use it you’ll have to install the supplementary driver located on the Windows XP CD. Windows XP includes Internet Information Services so you can easily setup a FTP to share files with friends or create your own web server. Obviously the Microsoft FrontPage extensions are provided with Windows XP and you can install them on-demand. FireWire cards can be used as network adapters and are natively recognized by Windows XP as network connections: all you have to do to establish a FireWire connection is to plug an IEEE 1394 between two PCs!
Microsoft Windows XP is the first operating system to support Wireless devices using the 802.11 (Wi-Fi) norm. Contrarily to previous releases of Windows, 802.11 devices are automatically recognized and need no configuration. Nonetheless Bluetooth adapters aren’t recognized nor managed by Windows XP. Thus accessing the network is instant and painless for users. When attempting to connect a laptop to a desktop using 802.11, Windows XP will automatically negotiate wireless network protocols and switch to the fastest connection. Plus you can implement the security of the 802.11 connections into an ActiveDirectory domain. Finally it’s possible for users to switch between static IP and DHCP configurations on the fly.
Microsoft Windows 98 SE came with the Internet Connection Sharing wizard which helps users set network connections easily. This feature has been enhanced in Microsoft Windows XP. The Internet Connection Sharing Wizard helps you share a single Internet connection with several PCs connected on a small network regardless of the operating systems they run; so you can save hardware and ISP costs. The Home networking wizard, introduced in Windows Me, has been replaced by the Network Setup Wizard. This wizard represents a single place to help users configure TCP/IP settings, workgroup memberships, and Internet Explorer settings at a glance.
It can also be used to define files, folders and printers sharing options as well as the included firewall. Windows XP perfectly supports multiple network adapters. One of the new Microsoft Windows XP network features is that when you share files, folders or disks a shared document folder will be automatically created. This folder will be accessible to every user and it’s just useful: instead of sharing a whole disk (to avoid the step of searching the folder you want to share) you can drag & drop files into the public document folder for easy sharing!
Internet Connection Sharing grants access to the most common network services like DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol), DNS (Domain Name System), NAT (Network Address Translation). Thanks to this extensive network support, the ICS will enable all downstream PCs to access the Internet through the home network. The Universal Plug & Play technology (first unveiled in Windows Me) enables automatic discovery of ICS hosts and their connection status.
Microsoft Windows XP includes another new feature to protect network connections. The ICF (Internet Connection Firewall) protects your computer from most of the threats that can come from an Internet connection (especially broadband connections). Common hacking attempts will be blocked by the integrated firewall but it’s clear the Firewall is a basic one and it won’t protect you from Trojan, DOS attacks, etc. Plus there’s no way to finely tweak the settings of the Firewall to block certain IPs, open or close some ports, etc. If the firewall is a welcome innovation for novice users, power users and hungry Internet surfers will clearly turn it off for a better firewall like Norton Personal Firewall.
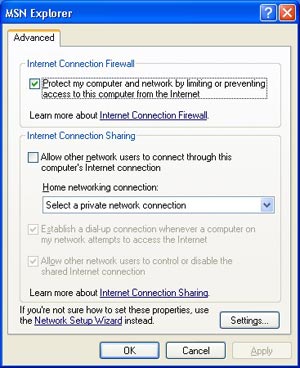
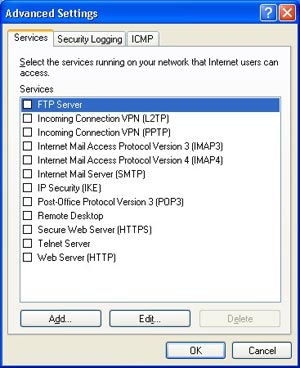
Windows XP
FireWall (click to enlarge)
Windows XP adopters can use the new EFS feature to encrypt files, a technology common to Home & Pro editions. Obviously any user can encrypt files on an NTFS formatted partition with EFS to secure their data. EFS isn't a new technology since it was already included in Windows 2000 but Windows 9x users will see this as a way to be much more secure with their information. EFS has been improved over Windows 2000: In Windows 2000, EFS could encrypt a file and only the individual that encrypted it could view it. Now the user that encrypted the file can select other users that can "Transparently" decrypt the file.
Mobile users will like the new offline files and folders feature offered by Windows XP Professional: that way users can define which network files or folder they need when they’re disconnected from the network in order to work with documents while being offline. One of the differences between the home and professional editions of Windows XP is that only owners of the Professional version can logon to Active Directory domains.
TCP/IP Properties have been improved quite a bit. The General Tab is essentially the same, but there is an additional tab that wasn’t there before. This tab only appears if you enable DHCP for your network connection. The tab is called Alternate Configuration. To understand how nice this feature you will need to understand what Automatic IP Addressing does. AIPA is for clients that are configured for DHCP and there is no DHCP Server available for them. The clients will automatically get an IP address from a class B Subnet identified with an IP Address in the range of 169.254.x.x so that they can communicate with each other if nothing else. This functionality was also built into Windows 2000 but the problem came in when half of your clients had leases from the DHCP Server before it went down. In that scenario, half of the computers could communicate with one another and the other half could not. You now have the option to manually configure an address for the client if a DHCP Server becomes unavailable.
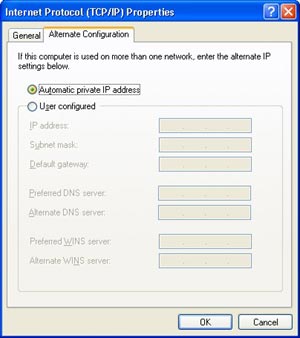
TCP/IP
Properties Dialog Box (click to enlarge)
If you look at the Status of a Network card (by double clicking on it, when it is connected to the network) XP allows you to do certain tests that were only available from the command prompt. One example of this is the Renew option. This command line switch was used alongside ipconfig to release a DHCP address and renew it. This is now available on the support tab of the network connection. The advanced button displays all of the information about your connection comparable to typing ipconfig /all from a command prompt. A new intriguing troubleshoot button appears in the network connection dialog box. If you select this option XP will open up the Help feature and display everything about your network connections.
Part of the help center of Windows XP is a new 'Network Diagnostics' feature. Those diagnostic tests will attempt to ping all DNS Servers, WINS Servers and the Default Gateway that you have configured for each adapter to make sure they properly work. If you wish, select the additional options and click the Start button to allow XP to gather additional information about you computer’s network configuration by re-executing the diagnostic tests. You can select additional information like the DNS Configuration, IP Address information, even whether or not your connections are DHCP enabled. Expanding the Computer System information even displays the hardware manufacturer of my computer and the model number associated with my system.
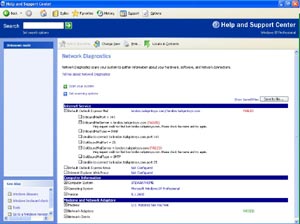
Windows XP
Network Diagnostics (click to enlarge)
Internet Connection
The ‘ceate a new internet connection’ wizard has been rewritten and now offers more logical options. This wizard offers four different ways to create an internet connection. If you want to connect to the internet using an ISP, select the first option. If you want to connect to a VPN at your office, go to option number two. The third option allows you to establish a connection with another computer as either the Host or Client while the fourth lets you fine tweak your connection, manually. Once you’ve chosen the option that match your need you just have to follow the steps indicated by the wizard by filling the various labels. If you have a broadband connection, a new broadband wizard will help you set up a permanent connection active from the startup of the computer. However this doesn’t work with every device especially with ADSL USB modems.
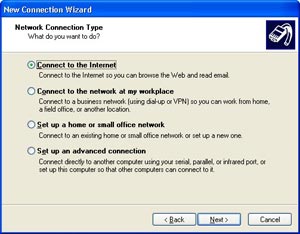
Microsoft
Windows XP New Connection Wizard (click to enlarge)
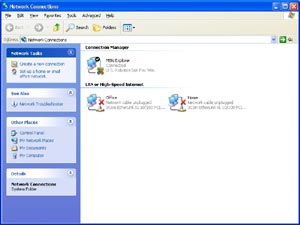
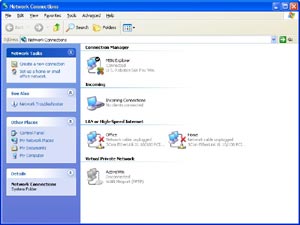
Windows XP Network Connections
(click to enlarge)



