|

|
| ActiveWin: Reviews | Active Network | New Reviews | Old Reviews | Interviews |Mailing List | Forums |
|
|
|
|
|
DirectX |
|
ActiveMac |
|
Downloads |
|
Forums |
|
Interviews |
|
News |
|
MS Games & Hardware |
|
Reviews |
|
Support Center |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2003 |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows XP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News Centers |
|
Windows/Microsoft |
|
DVD |
|
Apple/Mac |
|
Xbox |
|
News Search |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveXBox |
|
Xbox News |
|
Box Shots |
|
Inside The Xbox |
|
Released Titles |
|
Announced Titles |
|
Screenshots/Videos |
|
History Of The Xbox |
|
Links |
|
Forum |
|
FAQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Windows XP |
|
Introduction |
|
System Requirements |
|
Home Features |
|
Pro Features |
|
Upgrade Checklists |
|
History |
|
FAQ |
|
Links |
|
TopTechTips |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAQ's |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows 98/98 SE |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2002 |
|
Windows "Whistler" XP |
|
Windows CE |
|
Internet Explorer 6 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Xbox |
|
Xbox 360 |
|
DirectX |
|
DVD's |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TopTechTips |
|
Registry Tips |
|
Windows 95/98 |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Program Tips |
|
Easter Eggs |
|
Hardware |
|
DVD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveDVD |
|
DVD News |
|
DVD Forum |
|
Glossary |
|
Tips |
|
Articles |
|
Reviews |
|
News Archive |
|
Links |
|
Drivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Reviews |
|
Xbox/Games |
|
Fallout 3 |
|
|
|
Applications |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|
Windows 7 |
|
|
|
Hardware |
|
iPod Touch 32GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Interviews |
|
Steve Ballmer |
|
Jim Allchin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Site News/Info |
|
About This Site |
|
Affiliates |
|
Contact Us |
|
Default Home Page |
|
Link To Us |
|
Links |
|
News Archive |
|
Site Search |
|
Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credits |

|
Product:
Windows XP Professional Beta 2 |
Networking Features
|
Table Of Contents |
I am going to focus on TCP/IP for this section because it is the main protocol that most administrators work on. It is an open protocol that everyone uses to connect to the Internet.
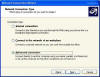
Network Connections are separated as shown in the above image. Network Cards are identified in the LAN or High-Speed Internet section. If you set up an Internet connection via a Dial-up modem, you will see it in the Connection Manager section of the screen. The Network Configuration Wizard is kept at the bottom where it belongs. When you open the wizard it looks like this:
The
Wizard separates everything in more of a logical manner than before.
If you want to connect to the internet using an ISP, select the first
option. If you want to connect to a VPN
at your office, go to option number two.
The third option allows you to establish a connection with another computer as
either the Host or Client.
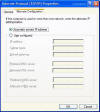
TCP/IP Properties have been improved quite a bit. The General Tab is essentially the same, but there is an additional tab that wasnít there before. This tab only appears if you enable DHCP for your network connection. The tab is called Alternate Configuration. To understand how nice this feature you will need to understand what Automatic IP Addressing actually is. AIPA is for clients that are configured for DHCP and there is no DHCP Server available for them. The clients will automatically get an IP address from a class B Subnet identified with an IP Address in the range of 169.254.x.x so that they can communicate with each other if nothing else. This functionality was also built into Windows 2000 but the problem came in when half of your clients had leases from the DHCP Server before it went down. In that scenario, half of the computers could communicate with one another and the other half could not. You now have the option to manually configure an address for the client if a DHCP Server becomes unavailable.
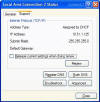
If you look at the Status of a Network card, by double clicking on it, when it is connected to the network, XP allows you to do certain tests that were only available from the command prompt. One example of this is the Renew option. This command line switch was used alongside ipconfig to release a DHCP address and renew it. This is now available on the support tab of the network connection. The advanced button displays all of the information about your connection, comparable to typing ipconfig /all from a command prompt.
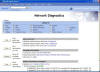
The Troubleshoot button is very intriguing. If you select this option, XP will open up the Help feature and display everything about your network connections, like the image below shows:
The
Screen shot that I have displayed here shows the options expanded on what you
can display in the Network Diagnostics pane.
When the diagnostic tests run, XP will attempt to ping all DNS Servers,
WINS Servers and the Default Gateway that you have configured for each adapter.
If you wish, select the additional options and click the Start button to
allow XP to gather additional information about you computerís network
configuration by re-executing the diagnostic tests.
You can select additional information like the DNS Configuration, IP
Address information, even whether or not your connections are DHCP enabled.
When I expanded the Computer System information, XP was able to identify
even the hardware manufacturer of my computer and the model number associated
with my system.
As you can see, Microsoft has really done a lot to improve Networking in Windows XP, but letís go on to one of the last common administrative tool that you use on a regular basis, the Task Manager.
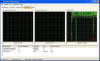
Task Manager
As you can see, there are two new tabs in the Task Manager. One is networking and the other is Users. Networking shows you all of your network adapters and what their current connectivity is. As you can see, at the time of this screenshot, I was downloading a lot of stuff over my modem, but nothing was occurring on either one of my LAN adapters. The Users tab shows which users are currently logged on.