
 |

|
| ActiveWin: Win LH | Active Network | Intro | FAQ | Win XP Tips | Compatibility List | Forum |
|
|
|
|
|
DirectX |
|
ActiveMac |
|
Downloads |
|
Forums |
|
Interviews |
|
News |
|
MS Games & Hardware |
|
Reviews |
|
Support Center |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2003 |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows XP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News Centers |
|
Windows/Microsoft |
|
DVD |
|
Apple/Mac |
|
Xbox |
|
News Search |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveXBox |
|
Xbox News |
|
Box Shots |
|
Inside The Xbox |
|
Released Titles |
|
Announced Titles |
|
Screenshots/Videos |
|
History Of The Xbox |
|
Links |
|
Forum |
|
FAQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Windows XP |
|
Introduction |
|
System Requirements |
|
Home Features |
|
Pro Features |
|
Upgrade Checklists |
|
History |
|
FAQ |
|
Links |
|
TopTechTips |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAQ's |
|
Windows Vista |
|
Windows 98/98 SE |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Windows Me |
|
Windows Server 2002 |
|
Windows "Whistler" XP |
|
Windows CE |
|
Internet Explorer 6 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Xbox |
|
Xbox 360 |
|
DirectX |
|
DVD's |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TopTechTips |
|
Registry Tips |
|
Windows 95/98 |
|
Windows 2000 |
|
Internet Explorer 5 |
|
Program Tips |
|
Easter Eggs |
|
Hardware |
|
DVD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ActiveDVD |
|
DVD News |
|
DVD Forum |
|
Glossary |
|
Tips |
|
Articles |
|
Reviews |
|
News Archive |
|
Links |
|
Drivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Reviews |
|
Xbox/Games |
|
Fallout 3 |
|
|
|
Applications |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|
Windows 7 |
|
|
|
Hardware |
|
iPod Touch 32GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Latest Interviews |
|
Steve Ballmer |
|
Jim Allchin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Site News/Info |
|
About This Site |
|
Affiliates |
|
Contact Us |
|
Default Home Page |
|
Link To Us |
|
Links |
|
News Archive |
|
Site Search |
|
Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credits |

Windows Vista Section - The State of Windows Vista (November 2005)
Two years ago, Microsoft intrigued Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) 2003 attendees with visions of dancing windows, an interface that cast off its ties to pixels and scaled to the highest resolution displays, and seamless integration of 2D, 3D, video and animation that would greatly enhance users' experiences without taxing their CPU. Later that year at the Professional Developer's Conference (PDC), Microsoft offered developers an updated view of Windows Vista and discussed its proposed featureset in great detail, asking the developer community for feedback that would help shape the new OS and directly contribute to the product's direction. This was the start of a long dialog that resulted in many changes to the original product roadmap. Previously Windows Vista-only technologies such as Avalon have made their way to down-level platforms due to direct feedback from the developer community. Likewise, WinFS has been separated from the Windows Vista roadmap so that customer-requested capabilities may be added without delaying the operating system's release. Several builds of the OS have since been distributed to developers, each build containing changes and improvements to Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), largely based on feedback.
With WinHEC 2004 came a new build, more details, and more enhancements to the codebase. The WinHEC 2004 build also offered (with minor tweaking) users the opportunity to personally experience the accelerated Window Manager and Compositor on their own hardware. Since WinHEC 2004, early versions of Avalon and Indigo were released via the WinFX SDK Community Technology Preview (CTP) for Windows XP/Server 2003, further extending the evaluation and feedback loop to the general public. The expanded availability of several Vista technologies to down-level platforms has prompted some people to contemplate just what Windows Vista will offer that makes it a compelling upgrade compared to current platforms when they are equipped with WinFX. The short answer is that while down-level platforms will receive WinFX, it will only be a subset of the WinFX APIs offered in Vista. Windows Vista will also include many new features and enhancements from the kernel up that will be exclusive to Vista. For those that remember, think of down-level WinFX as analogous to Win32s which allowed partial API compatibility between Windows NT and Windows 3.1. With Win32s, developers could create 32-bit applications that ran on both Windows 3.1 and NT. However, while Windows 3.1 received some application compatibility, it did not receive the platform or user interface enhancements contained within Windows NT or Windows 9x.
At WinHEC 2005, Microsoft announced the completion of the Windows Vista driver model. Beta 1 was released in July 2005 and contained roughly 1/3 of the features expected for the final release -- mostly developer-oriented. The release to manufacturing (RTM) is scheduled for 2006. In this article, we'll cover some of the features that make Windows Vista a worthwhile upgrade based upon currently known details about the platform. This is by no means a complete listing of expected Windows Vista features. Look to this section for future updates and to the ActiveWin.com homepage for the very latest in our continuing coverage of Windows Vista.
-- Jonathan Tigner
Preliminary information -- subject to change.
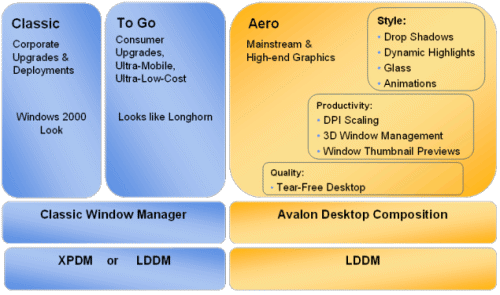
Windows Vista includes multiple graphical experience tiers that will be available to the end-user based on their hardware capabilities:
Classic
Classic is the base graphical experience offered in
Vista.
The minimum display hardware requirements for the Classic experience
include:
Aero Experience
The Aero Experience-capable minimum display hardware requirements
for both discrete and UMA solutions include:
- 64 MB of memory available for graphics.
- A minimum 1024x768 resolution (1280x600 resolution is acceptable for wide-aspect ratio displays).
- A minimum of 32 bpp.
- A DirectX 9-class GPU that supports Pixel Shader 2.0.
When the display solution is based on UMA, the system RAM must be DDR RAM to provide sufficient bandwidth for scaling on high-DPI monitors. UMA-based solutions must allow the GPU to lock at least 64 MB of system memory to be used by the GPU. At a minimum, an Aero Express-capable solution must have a signed driver that implements the Windows Vista Display Driver Model required for Aero Express experience. The Aero Express experience will not run with earlier display drivers.
Aero Glass Experience
The Aero Glass-capable minimum display hardware requirements
for both discrete and UMA solutions include:
- 64 MB of memory available for graphics.
- A minimum 1024x768 resolution (1280x600 resolution is acceptable for wide-aspect ratio displays).
- A minimum 32 bpp.
- A DirectX 9-class GPU that supports Pixel Shader 2.0.
When the display solution is based on UMA, the system RAM must be DDR RAM to provide sufficient bandwidth for scaling on high-DPI monitors. UMA-based solutions must allow the GPU to lock at least 64 MB of system memory to be used by the GPU. At a minimum, an Aero Glass-capable solution must have a signed driver that implements the Windows Vista Display Driver Model required for Aero Glass experience. The Aero Glass experience will not run with earlier display drivers.
Diamond
Diamond is the codename referring to the graphical experience
associated with the Windows Vista Media Center interface.
The Diamond-capable minimum display hardware requirements
for both discrete and UMA solutions include:
- A Windows Graphics Foundation-class GPU
At a minimum, a Diamond-capable solution must have a signed driver that implements the Windows Vista Display Driver Model required for Diamond experience. The Diamond experience will not run with earlier display drivers. The Diamond experience is built specifically around the functionality provided by the Windows Graphics Foundation.
Windows Explorer / Information Visualization & Organization
Virtual Folders
Virtual Folders are similar to normal file folders in Windows except the files they contain are based on dynamic queries. Users can create virtual folders that list files based upon any attribute (such as Author, Keyword, etc.) of the files you want the virtual folder to contain. Usage of virtual folders may be similar to Outlook 2003's search folders.
Search
In Windows Vista, users can search directly from the start menu. Click the Start button, enter a search query and have results immediately returned within the start menu's item pane. This feature can also be used to execute applications. This is great for starting applications that may be nested several level into the start menu. This capability is similar to that currently offered by MSN Desktop Search.
Vista's Explorer allows users to not only execute fast searches to find their data, but also has several features and methods that allows users to build relationships around their data, group files according to personal preference, and visualize files without opening its associated application. All of this increases user productivity and decreases the time it takes to find the right information.
Lists
Users can create ordered lists of files that they want to keep together. The lists contain references (shortcuts) to the files instead of the actual files themselves. This is great for working with data that is located across several computers. Lists can be sent to other users (via email for example) and allowing all users in a group to keep a set of files together while always having access to the latest version of those files. Windows Vista Beta 2 will support using lists to access documents published via RSS feeds and internet sites.
Live Icons
In Windows Vista's Explorer, icons are not just static images. The icons are now live, scalable views of the actual document, allowing you to quickly and easily find the correct document you need.
Preview Pane
In Windows Vista's, Explorer windows have a preview pane at the bottom that presents relevant information about currently selected directories or documents and allows users to quickly modify document metadata.
Windows Sidebar
The Windows sidebar is a future technology which allows mini-applications called 'gadgets' to reside on the desktop. Gadgets are mirco-applications written using either the Windows API or standard web technologies which allow the user instant access to any and all information imaginable. These micro-applications reside either in the Windows sidebar, which docks unobtrusively to the side of the desktop, or they can float freely on the desktop, providing users with access to content.
While Aero and Diamond provide the most visible changes to Windows Vista, the features that fall under the category of "Fundamentals" provide a more universally compelling case for adopting the new OS.
Protected User Accounts
Since its first release, Windows NT has had a robust, granular security model capable of restricting applications from running with full privileges. Unfortunately, due to the existence of applications that won't run without requiring administrative privileges at some point, the default user account for most Windows installations is an administrator. Due to the defaults and the possible troubles of running as a normal user, generally, only businesses and some power users take full advantage of the security model and run with least privilege. With Vista, Microsoft seeks to change the current situation and make it much easier to run as a normal user on Windows systems. They will accomplish this primarily via two fronts. The first change involves getting more developers to code and test their applications while running as a normal user. Second, the security model is being extended in Windows Vista to not only make it easier to run with least privilege when using normal applications, but also to limit a user's exposure while running applications that require elevated privileges.
LUA -- Limited User Account
In Windows Vista, user tokens will be split between the application and the user. Even if you login as an administrator, LUA apps run as a limited user.
Application Impact Management
Application Impact Management (AIM) manages
applications that make changes to the system. Vista monitors system changes
(files, folders, registry settings, etc.) and can roll them back.
PA -- Protected Administrator
On Windows Vista, administrators also run with least privilege. Applications requiring administrator privileges will run with elevated privileges. Only trusted applications can run with elevated privileges. By default, these applications must have a signed manifest to be trusted to run with elevated privileges. Manifests can be automatically generated for most legacy applications, however, some applications may break if AIM cannot make it run without administrator privileges. In this case, the Administrator may intervene and designate the application as trusted and allow it to run with elevated privilege.
Code Access Security
Windows Vista builds on the managed code infrastructure of .NET. Therefore, it offers the same Code Access Security (CAS) base that allows code to be verified based on evidence that extends beyond the currently running user. Code can be given or denied execution permission based on a number of factors such as its location, whether it is signed, or by whom it is published. This evidence is also combined with policies set by the administrator to determine whether the code can be executed. CAS makes it possible to run code that can be restricted to having a set of privileges below even that of a normal user.
Secure Execution Environment
The Secure Execution Environment (SEE) is the default set of CAS permissions for Windows Vista. Security is enforced via the Common Language Runtime (CLR). Only safe operations possible in the SEE. SEE permissions are similar to the permissions set .NET applications executed from the Internet Zone have today. Only a set of trusted libraries may be called in the SEE. Only isolated storage is available (applications cannot obtain file path information). Only trusted operations are allowed (file access, for instance, requires the user to use the file open dialog to give the application the file). Applications may request elevated privilege, if necessary, via a standard user interface. Applications may also restrict themselves to a subset of available permissions to further limit possible attack vectors.
Virtualization of Protected Resources
Access to protected resources is virtualized. Sandboxing is used for COM component extensions such as Windows Explorer shell extensions or Internet Explorer ActiveX controls. This helps to protect the host application from being crashed by an extension. Extensions can be enabled or disabled through attestation.
Windows Login
Winlogin (GINA) is being rewritten for Windows Vista to reduce
number of necessary processes and components loaded. The new GINA will not
be replaceable. A new Credential Provider Model will be used for extensibility.
New mechanisms will also be provided to support existing functionality.
A new Eventing and Stacking, and Chaining model will be provided.
Trusted Platform Module Services
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a
microchip designed to provide certain basic security-related functions to
the software that utilizes TPM. The next version of Microsoft® Windows®,
Vista, provides a set of services for applications that use TPM technologies. TPM
Services in Windows Vista enable the development of several
kinds of applications that provide significant value for customers. For
example:
- Data protection and security. Examples of applications that help
secure customer data include:
- Key management utilities
- Document-signing applications
- Data protection/encryption applications
- Attestation services
- Key management utilities
- System administration. Examples of applications that help administrators
control TPMs in the enterprise include:
- Remote Administration through WMI
- Group Policy
- Easy deployment and decommissioning
- Remote Administration through WMI
- System security for end users. Innovative features that are based
on TPM technology in Windows Vista include:
- Secure Startup
- TPM-based Key Storage Provider
- Secure Startup
A detailed white paper about Trusted Platform Module Services is available for download: Trusted Platform Module Services in Windows Vista
Secure Startup
Secure Startup is a hardware-based security feature that
addresses the growing concern for better data protection. The feature uses
a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 to protect user data and to ensure that
a computer running Windows Vista has not been tampered with while the system
was offline. Secure Startup provides both mobile and office enterprise information
workers with more data protection when systems are lost or stolen. Detailed
white papers about NAP is available for download:
Secure Startup - Full Volume Encryption: Executive Overview |
Secure Startup - Full Volume Encryption: Technical Overview.
Network Access Protection
Network Access Protection (NAP) for Windows Server
"Longhorn"
is a new set of operating system components that provide a platform for
protected access to private networks. The NAP platform provides an integrated
way of detecting the state of a network client that is attempting to connect
to a network and restricting the access of the network client until the
policy requirements for connecting to the network have been met.
To protect access to a network, a network infrastructure needs to provide
the following areas of functionality:
- Policy validation Determines whether the computers are compliant with security policy. Compliant computers are deemed “healthy.”
- Network restriction Restricts access based on health state.
- Remediation Provides necessary updates to allow the computer to get healthy.
- Ongoing compliance Permits access to the network as long as the users’ computer meets policy requirements.
The NAP platform provides enforcement for Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) address configuration, virtual private network
(VPN)-based network connections, and Internet Protocol security (IPsec)-based
communications and an architecture through which policy validation, network
restriction, remediation, and ongoing compliance can occur via additional
components supplied by third-party software vendors or Microsoft.
The NAP platform requires servers running Windows Server "Longhorn" and
clients running Windows® XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2). A detailed white
paper about NAP is available for download
here.
Performance and Reliability
Device Drivers
Windows Vista introduces a new, simplified device installation architecture that is more user-friendly, more flexible, and more secure than device installation for previous versions of Windows. This new device installation architecture solves problems with device installation on earlier versions of Windows, including issues related to client-side installation, missing files, digital signatures, and permissions needed to install drivers.
Windows Vista Device Installation Architecture
Under the Windows Vista device installation architecture,
devices and kernel-mode device drivers can be installed only through
approved device installation functions. These functions restrict an
external component's ability to access or modify the internal resources
of the device (the registry settings and files used for device
installation) through unsupported means.
Using these functions ensures that driver installation packages cannot
take actions that might conflict with other device installations,
applications, or Windows components, and that any installed driver can
be rolled back cleanly or uninstalled in the event of problems. Many of
the rules that driver packages must follow to be installed successfully
in Windows Vista represent best practices for Windows Server 2003, Windows
XP, and earlier versions of Windows. Existing driver packages that
implement these best practices should require few if any changes to work
for Vista.
Driver packages designed to the Windows Vista device installation architecture help to ensure that drivers and associated applications are removed cleanly, without leaving files, state, or registry settings on the system that might cause instability or loss of functionality. Such driver packages also help preserve the stability and functionality of the system over time, as more devices are installed and uninstalled.
A new Driver Store holds complete device driver packages on disk. The packages are validated and checked for dependencies up front to mitigate the issue of problem drivers entering the Driver Store. The Driver Store and new installation rules eliminate partial driver installation scenarios where a driver may only install some components, then later prompt the user for a CD or the location of the source package to continue installation. This prevents situations where the user may no longer have access to the source media after an initial installation. Only driver packages located within the Driver Store may be installed.
Windows Driver Foundation
The Windows Driver Foundation (WDF) is a new
object-oriented, event-driven driver model that includes several
components:
WDF is designed to simplify device driver development by providing a
single model for user-mode and kernel-mode driver development. User-mode
driver developers now have a common infrastructure for driver
development, and kernel-mode driver developers have a unified driver
model for multiple device classes that abstracts them from
platform-specific structures without sacrificing performance. This
abstraction serves to better shield driver developers from incremental
changes in new operating system releases that may otherwise introduce
incompatibilities or limit Microsoft's implementation flexibility, and
it lays the groundwork for future isolation of
kernel-mode drivers from the OS. Under driver isolation, a kernel-mode
driver runs in a protected environment. If the driver crashes, the
system cleans up any resources allocated by the driver and recovers
without crashing or halting the system. WDF supports versioning so
that a single driver binary can run on any version of the operating
system and use the same version of the framework with which it was built
and tested. WDF also supports side-by-side execution. WDF will be
supported on Windows 2000 and above platforms.
Driver Quality Signature
Windows Vista enables installation of device drivers by
non-administrator users. An installation rules engine checks the user's
driver installation policy to determine whether or not to permit
installation. Device drivers must be signed by a trusted source to allow
non-administrator installation. Device drivers may be signed by
Microsoft via the "Designed for Windows" Logo Program or Driver Quality
Signature Program, or they may be signed by the hardware vendor or
system administrator using Microsoft Authenticode technology. A local
administrator can sign a driver package that is trusted on that system
only; a domain administrator can sign a driver package that is trusted
within that domain. Authenticode signing allows administrators to
identify the publishers of all driver packages installed on a system and
to verify that driver packages were not altered after publication.
Because all driver packages are signed in one way or another, signatures
no longer affect the rank of a driver for Plug and Play.
Power Management
The are several changes and enhancements in the area of power management on Windows Vista. A new kernel power manager called the Device Power Policy Engine (DPPE) maintains and coordinates power policy behavior on behalf of devices and applications. The DPPE provides notifications about power policy, power state, thermal events, etc. Power policy is set by the user either by selecting one of the default power policies (e.g., Maximum Battery, Automatic, Maximum Performance), or by defining a custom policy. Applications can respond to changes in power state or policy, for example, Windows Explorer could transition to a less graphically intense shell to conserve battery power if the Maximum Battery policy is set.
XML Paper Specification (XPS) “Metro” Document Technologies
XPS print path (codenamed 'Metro') is a family of technologies developed by Microsoft that provides a unified framework to address the growing use of electronic document-based workflows, and inclusion of advanced graphics and extended color information in everyday documents and Web applications. “Metro” offers an open document format that uses Extensible Markup Language (XML) and other current, industry standards to create a modern, cross-platform document and imaging technologies. “Metro” simplifies creation, sharing, printing, viewing and archiving of digital documents, while also improving image fidelity and print performance.
“Metro” provides an authoring and information exchange
platform to support the new document format. The complete family of
technologies includes the following:
- A complete specification for a fixed-layout document format based on XML that offers “electronic paper” for use by any application on any platform
- A “viewer” to view, manage and print files
- A print-to-file converter for creating the files from any Microsoft® Windows-based application
- A set of application programming interfaces (APIs) to incorporate “Metro” technologies and documents with traditional applications, the Web and computer hardware
- A print pipeline with an integrated spool format and printer-page description language to speed up and improve the fidelity of print jobs
- An updated driver model for “Metro”-consuming printers
“Metro” provides a unified and open way to create and utilize fixed-format documents from existing information worker applications. It also enables Web, application and hardware developers to unite their document, imaging and printing formats. “Metro” uses XML to describe how a document should be rendered. It also uses openly available fonts and images and dictates how the components of a document should be stored in .ZIP File Format Specification. As a result, “Metro” can be used on any platform, and any .ZIP implementation can be used to view the components of the Metro file. Microsoft plans to offer a royalty-free license for “Metro” when the specification and documentation are final. The license will enable vendors to integrate “Metro” technologies for creating and utilizing documents into applications or hardware, creating a consistent format for end-to-end document workflows. “Metro” is planned to be delivered as part of Windows Vista and WinFX in the second half of 2006. The “Metro” specification is available for download: Metro Specification
Windows Color System
Windows Vista will provide a new foundation to cover
advanced color management needs for the next decade. The new WCS will
integrate state-of-the-art understanding of the human visual system with
a componentized and flexible infrastructure. Microsoft will also offer
significant enhancements to the user experience by making end-user
control of color variables centralized, intuitive, and easy to use.
-
The new features of the WCS in Windows Vista include:
- A completely revamped color infrastructure and translation engine (CITE). CITE is the core of a novel color management paradigm that is modular, transparent, unambiguous, and understandable.
- An unparalleled extensibility framework through which imaging IHV and ISV partners can enhance and improve the components of the CITE for their business-critical scenarios.
- An enhanced color processing pipeline with support for greater bit depths, multiple color channels, and alternative color spaces.
- Seamless interoperability with ICC-based workflows, including continued support for current ICM2 application programming interfaces (APIs) and sRGB (standard red-green-blue), with extended APIs to support new functionality.
- A significantly improved user experience through a centralized color control panel and an intuitive and easy-to-use monitor calibration wizard.
- Important enhancements to Microsoft imaging codecs, as well as key improvements to the core color management and print infrastructure to support very specific target scenarios such as enterprise color printing and out-of-box digital photography.
A detailed white paper about WCS is available for download: Windows Color System in Windows Vista
Windows Vista Display Driver Model
The Windows Vista Display Driver Model (LDDM) provides performance, stability, security, and reliability enhancements over the display driver model provided in Windows XP. The XP driver model is still supported in Windows Vista, but only for compatibility. There are two driver models that compose what is collectively known as the Windows Vista Display Driver Model. There is the Basic Driver Model and the Advanced Driver Model. The Basic Driver Model provides support for the features of current graphics hardware, while the Advanced Driver Model provides support for new features that will be available in Windows Vista-era graphics hardware.
Graphics Hardware Virtualization and Application Graphics State Isolation
The LDDM provides a virtual address space for graphics hardware, separating each application's graphics resources and rendering state. Graphics command streams are validated to prevent unauthorized used of one application's graphics resources from another application, and to prevent sending bad commands to the hardware. Command stream validation is performed in software with the Basic Driver Model, whereas graphics adapters supporting the Advanced Driver Model will perform this validation in hardware. A memory manager determines which application resources need to reside in memory. Application resources may exist in graphics memory, system memory, or a page file. Advanced Driver Model hardware supports demand paging. Resources can be paged in or out of memory as necessary. Data is not duplicated between storage levels. For applications using the Windows Graphics Foundation APIs, application resources can be larger than available video memory.
The LDDM virtualizes access to graphics devices. A scheduler controls access to the GPU(s), allowing multiple applications to use the GPU as a shared resource similar to how CPUs are used today. There are two methods for scheduling depending on the driver model used. The Basic Driver Model uses batch scheduling. Batches consist of a sequence of commands submitted by an application. Once a batch is executed, it cannot be interrupted. Scheduling in the Advanced Driver Model is based on application contexts. The Advanced Driver Model scheduler may interrupt commands executing in one application context to execute commands from a different context that may have higher priority. Because there is no blocking (i.e., having to wait for one batch of commands to finish before moving to a new batch), hardware that supports the the Advanced Driver Model can provide a more responsive experience for end-users.
Graphics device virtualization opens up new scenarios such as hot-plug insertion and removal of graphics hardware (on hot-plug supporting systems), allowing GPU insertion or removal and configuration (new driver installation) without requiring a reboot.
Graphics APIs
Windows Vista supports the new Windows Graphics Foundation (WGF) APIs as well as OpenGL and legacy Direct3D interfaces.
Direct3D Legacy
Windows Vista's Direct3D interface matches DirectX 9.0c.
Direct3D application resources are limited to the size of available
video memory to maximize compatibility. Memory virtualization is largely
hidden from Direct3D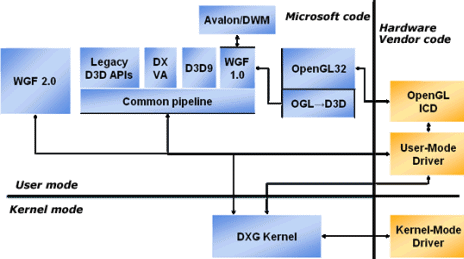 applications, and these applications would need to be ported to the
Windows Graphics Foundation to benefit from full virtualization. Older
Direct3D immediate mode APIs are also supported by mapping their
interfaces to those of Direct3D 9.0.
applications, and these applications would need to be ported to the
Windows Graphics Foundation to benefit from full virtualization. Older
Direct3D immediate mode APIs are also supported by mapping their
interfaces to those of Direct3D 9.0.
OpenGL
Out of the box, OpenGL will be hardware accelerated via the Windows Graphics Foundation 1.0. Hardware vendor Installable Client Drivers (ICDs) will continue to be supported in Windows Vista under both the Windows XP and Windows Vista display driver models.
Windows Graphics Foundation
Windows Graphics Foundation 1.0 and 2.0 will be included in Windows Vista. WGF 1.0 is an enhanced version of Direct3D 9.0 supporting managed memory resources, cross-process surface sharing, extended gamma range, and text antialiasing.
Desktop Window Manager
The Windows Vista Desktop Window Manager (DWM) is built upon the Windows Graphics Foundation 1.0 interfaces and is responsible for compositing application client areas with non-client areas provided by the DWM. The Desktop Window Manager supports high-dpi displays, video playback, animation, and shaders. Cross-process shared surfaces support in WGF 1.0 allows the Desktop Window Manager to access the back buffers of applications. The DWM turns off when running certain applications, such as those that use overlays or front buffer rendering. Cross-process surface sharing also benefits full-screen exclusive and multiple monitor applications. Instead of full-screen exclusive applications "owning" the GPU, causing other applications to lose device access, the exclusive application now simply gains control of the display output from the Desktop Window Manager. Display resolution, gamma, etc., are controlled by the exclusive application, but background applications maintain access to their resources and continue to run normally. If necessary, the exclusive application is given higher priority than the background processes. In multiple monitor scenarios, each monitor has its own desktop, and display output control is independent for each monitor.
Windows Graphics Foundation 2.0
Windows Graphics Foundation 2.0 is the next generation
of Direct3D:
The combination of LDDM and WGF 2.0 represent a major enhancement for
high-performance graphics on the Windows platform.
Windows Vista Media Enhancements
Content Protection & Protected Video Path
Windows Vista supports several methods for protecting digital media, which should help to increase the availability of commercial media on the PC. Technologies, like CableCard, which have largely been limited to use in set-top boxes can now have similar content security assurances on the PC. This security is offered via the Protected Media Path (PMP) and the Protected Video Path (PVP). Graphics devices are "trusted" via device and device driver authentication. Encryption is used to protect content as it travels over user-accessible buses. Standard output protection methods, such as HDCP, HDMI, etc., are used to protect content as it is output to display devices.
Glitch-Free Media Support
Glitch-Free Media Support is achieved via enhancements
in several areas including:
Windows Vista Audio
Windows Vista will have a new user-mode, high-fidelity
audio engine designed for high-quality and easy extensibility. Some
features of the audio engine include:
The new user-mode audio stack will replace the kernel-mode stack while providing increased platform resiliency and maintaining legacy audio support.
Windows Vista Video
Windows Vista also provides an enhanced platform for
video:
Plug 'n' Play Extensions (PnP-X)
PnP-X extends Windows PnP services and allows
virtually connected devices to be integrated into the Windows PnP
subsystem.
This natural progression of device support in Windows solves
the following problems:
PnP-X unifies the device experience in Windows Vista, making device
discovery, installation, and use the same regardless of its method of
attachment to the computer.
Currently, physically
connected devices appear in Device Manager and UPnP certified devices
appear in My Network Places. This leads to additional customer
confusion.
Cellular Phone Connectivity
Windows Vista
will extend cellular phone connectivity options and provide an integrated experience for end-users. Some possible scenarios include:- Media and information synchronization
- Image acquisition
- File browsing and transfer
- Use device for remote control of PC applications
- Use device as an auxiliary display
- Forward PC notifications to a device
Platform Virtualization
Windows Virtualization Architecture
Windows Vista will support hypervisor-based
platform virtualization. Some proposed features include:
Server-specific features
The Windows Virtualization Architecture will require hardware support
via Intel's VT or AMD's "Pacifica" virtualization assistance
technologies. Microsoft will provide well-defined, published interfaces
to allow third-parties to provide support for other OSes as guests.
The new Windows File System (WinFS) will enter beta testing around the time of Windows Vista's retail release, and will be available as an update to Windows Vista following it's retail availability. WinFS lets users build relationships between various data such as Microsoft Word documents, emails, contact information, appointments, web pages, and other data types. It provides storage for non-file-backed items, increased data extensibility and accessibility through the use of standardized schemas. WinFS provides access to a universal storage platform that can span multiple local or networked sources, providing general purpose and domain-specific data management and synchronization.
With Windows Vista, transactions become a fundamental part of the platform with the inclusion of the Kernel Transaction Manager (KTM). This service is leveraged to provide full ACID transactional support for local and remote file shares. Check here for more info on Transactional NTFS.
Images Copyright Microsoft Corporation.
![]()
Return To The Windows Vista Section
